Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (41): 6567-6572.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.41.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Survival and growth of nano-bioprobe double-labeled rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Cao Ai-hong1, 2,Yang Xin1, Guo Zi-wei1, Hu Wei1
- 1Department of Radiology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Functional Imaging, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-09-08Online:2014-10-01Published:2014-10-01 -
Contact:Cao Ai-hong, Department of Radiology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221006, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Functional Imaging, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Cao Ai-hong, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Radiology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221006, Jiangsu Province, China; Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Functional Imaging, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Plan Project of Xuzhou City, No. XM12B043
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Ai-hong,Yang Xin, Guo Zi-wei, Hu Wei. Survival and growth of nano-bioprobe double-labeled rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6567-6572.
share this article
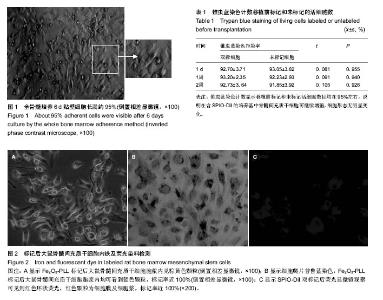
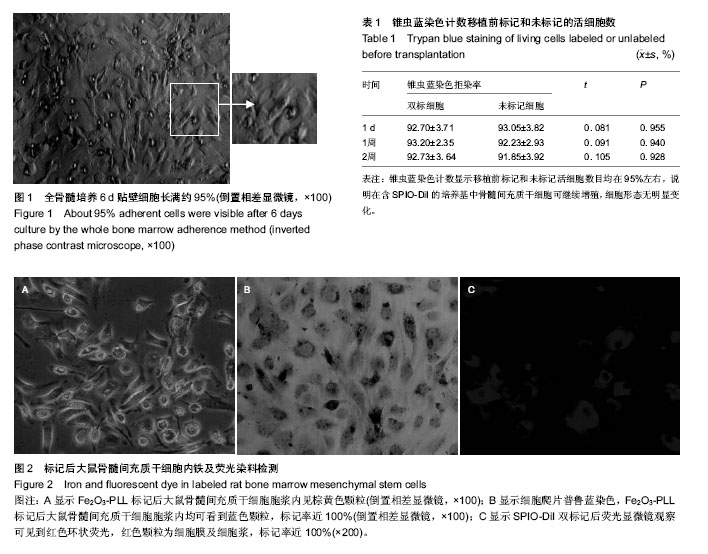
2.1 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞培养纯化及形态学观察 原代培养的细胞,48 h第1次换液见部分细胞贴壁,呈圆形或卵圆形,换液逐渐去除未贴壁细胞,全骨髓培养经过3-5 d、密度梯度离心法经过6-8 d的静止期,细胞逐渐伸出伪足,多数为成纤维样梭形或多边形细胞,大部分为单核,位于细胞中央,呈集落生长,细胞增殖迅速,集落相互靠近,慢慢融合,于培养9至10天(全骨髓培养法)、13-15 d(密度梯度离心法)渐渐铺满培养瓶。传代培养的细胞24 h完全贴壁,第1代的生长周期为五六天,随着传代次数增多,细胞形态越来越均匀,没有明显变化(图1)。传代后细胞四五天即可长满融合,以继续传代扩增。 2.2 流式细胞仪细胞表面标志测定 流式细胞仪结果显示实验分离培养的骨髓间充质干细胞均一性好,达99%以上CD29+、CD90+、CD45-,说明传代贴壁生长的梭形细胞确为骨髓间充质干细胞。 2.3 骨髓间充质干细胞多能横向分化潜能鉴定 成脂肪诱导:诱导3 d后,细胞由成纤维细胞样逐渐收缩变短,成为立方形或多角形;连续培养7 d,镜下可见细胞内有微小脂滴出现,随着时间的延长,脂滴逐渐增大融合,培养2周时,可见融合成团的脂滴充满整个细胞,油红O染色,可见细胞内大量红色脂滴。 成骨诱导:培养1周后,细胞形态明显改变,由成纤维细胞样变为多角形,类似神经元细胞,细胞周边出现长丝状突出,向周围延伸。培养2周以上,细胞基质矿化物逐渐出现,培养4周以上,可见明显钙化结节,von Kossa染色可见钙盐沉积区域呈黑色。 2.4 Fe2O3-PLL磁性纳米粒子的表征分析 将合成的产物经透射电镜观察,nano-Fe2O3-PLL呈球形,分布均匀。直径分布为10-20 nm,平均直径为16 nm,具有立方尖晶石的晶体结构。饱和磁化强度为60 emu/g。 2.5 SPIO-DiI双标记后细胞内铁及荧光染料检测 标记后的活细胞在倒置相差显微镜下已能见到胞浆内的棕黄色颗粒(图2A),细胞爬片普鲁蓝染色后,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的几乎每个标记细胞浆内均可看到蓝色颗粒,标记率近100%(图2B),而未标记细胞内无蓝色颗粒。荧光显微镜观察,可见到红色环状荧光,红色颗粒为细胞膜及细胞浆,中间未染色的为不着色的细胞核,几乎每个标记细胞均可看到红色荧光,标记率近100%(图2C)。 2.6 双标对骨髓间充质干细胞活力及增殖的影响 锥虫蓝染色计数显示移植前标记和未标记活细胞数目均在95%左右(表1),说明在含SPIO-DiI的培养基中骨髓间充质干细胞可继续增殖,细胞形态无明显变化。"
| [1] Weissleder R.Molecular imaging: exploring the next frontier.Radiology. 1999;212(3):609-614.
[2] Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR,et al.Intracytoplasmic tagging of cells with ferumoxides and transfection agent for cellular magnetic resonance imaging after cell transplantation: methods and techniques.Transplantation. 2003;76(7): 1123-1130.
[3] Beyer Nardi N, da Silva Meirelles L.Mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, in vitro expansion and characterization.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(174):249-282.
[4] Koide Y, Morikawa S, Mabuchi Y,et al.Two distinct stem cell lineages in murine bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2007;25(5): 1213-1221.
[5] Baksh D, Song L, Tuan RS.Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8(3):301-316.
[6] Minguell JJ, Erices A, Conget P.Mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2001;226(6):507-520.
[7] Oswald J, Boxberger S, Jørgensen B,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):377-384.
[8] Barry FP, Murphy JM.Mesenchymal stem cells: clinical applications and biological characterization.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36(4):568-584.
[9] Minguell JJ, Erices A.Mesenchymal stem cells and the treatment of cardiac disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006; 231(1):39-49.
[10] Liang F, Wang YF, Nan X, et al.In vitro differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into blood vessel endothelial cells.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2005;27(6):665-669.
[11] Gang EJ, Jeong JA, Han S,et al. In vitro endothelial potential of human UC blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(3):215-227.
[12] Alviano F, Fossati V, Marchionni C,et al.Term Amniotic membrane is a high throughput source for multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells with the ability to differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro.BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:11.
[13] Lansdorp PM, Dragowska W, Mayani H.Ontogeny-related changes in proliferative potential of human hematopoietic cells.J Exp Med. 1993;178(3):787-791.
[14] Krupnick AS, Balsara KR, Kreisel D,et al.Fetal liver as a source of autologous progenitor cells for perinatal tissue engineering.Tissue Eng. 2004;10(5-6):723-735.
[15] Hao HN, Zhao J, Thomas RL,et al.Fetal human hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate sequentially into neural stem cells and then astrocytes in vitro.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003; 12(1):23-32.
[16] Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S,et al.Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow.Blood. 2001;98(8):2396-2402.
[17] 赵明,任彩萍.胚胎干细胞诱导分化的研究进展[M].生命科学, 2005,17(1):19-24.
[18] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al.Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow.Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.
[19] 何朝荣,张群林,黄从新.兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外成内皮细胞能力的研究[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2003,2(4) :287-291.
[20] 崔磊,于海莹,尹烁,等.诱导大鼠骨髓内皮祖细胞成内皮细胞的体外增殖规律的观察[J].中华实验外科杂志,2004,21(6):652-653.
[21] 肖海波,梅举,张宝仁,等.大鼠骨髓基质干细胞体外诱导向内皮分化的实验研究[J].上海医学,2005 ,28(3):227-229.
[22] Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T,et al.Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans.Circulation. 2002; 106(15):1913-1918.
[23] Englund U, Fricker-Gates RA, Lundberg C,et al.Transplantation of human neural progenitor cells into the neonatal rat brain: extensive migration and differentiation with long-distance axonal projections.Exp Neurol. 2002;173(1):1-21.
[24] Terada N, Hamazaki T, Oka M,et al.Bone marrow cells adopt the phenotype of other cells by spontaneous cell fusion. Nature. 2002;416(6880):542-545.
[25] Fraser JK, Schreiber R, Strem B,et al. Plasticity of human adipose stem cells toward endothelial cells and cardiomyocytes.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006;3 Suppl 1:S33-37.
[26] Fuchs S, Baffour R, Zhou YF,et al.Transendocardial delivery of autologous bone marrow enhances collateral perfusion and regional function in pigs with chronic experimental myocardial ischemia.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37(6):1726-1732.
[27] 孔炜伟,滕皋军.体外培养人胎肝细胞与永生化L-02肝细胞的生物学性状比较[J].中华放射学杂志,2004,38(2):119-123.
[28] 王悍,滕皋军,缪竞陶,等.酸性成纤维细胞生长因子和肝细胞生长因子在肝干细胞分化成熟中的作用[J].中华放射学杂志, 2004, 38(2):124-128.
[29] Bengel FM, Schachinger V, Dimmeler S.Cell-based therapies and imaging in cardiology.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005; 32 Suppl 2:S404-416.
[30] Hill JM, Dick AJ, Raman VK,et al. Serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of injected mesenchymal stem cells. Circulation. 2003;108(8):1009-1014.
[31] Wickline SA, Lanza GM.Nanotechnology for molecular imaging and targeted therapy.Circulation. 2003;107(8): 1092-1095.
[32] Kamihata H, Matsubara H, Nishiue T,et al.Implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells into ischemic myocardium enhances collateral perfusion and regional function via side supply of angioblasts, angiogenic ligands, and cytokines. Circulation. 2001;104(9):1046-1052.
[33] Hamano K, Nishida M, Hirata K,et al.Local implantation of autologous bone marrow cells for therapeutic angiogenesis in patients with ischemic heart disease: clinical trial and preliminary results.Jpn Circ J. 2001;65(9):845-847.
[34] Wang JS, Shum-Tim D, Galipeau J,et al.Marrow stromal cells for cellular cardiomyoplasty: feasibility and potential clinical advantages.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;120(5):999-1005.
[35] Ju S, Teng GJ, Lu H,et al.In vivo MR tracking of mesenchymal stem cells in rat liver after intrasplenic transplantation. Radiology. 2007;245(1):206-215.
[36] Sun JH, Teng GJ, Ju SH, et al.MR tracking of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in rat kidneys with acute renal failure.Cell Transplant. 2008;17(3):279-290.
[37] Wang DS, Dake MD, Park JM, et al.Molecular imaging: a primer for interventionalists and imagers.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17(9):1405-1423.
[38] 居胜红,滕皋军,毛曦,等.脐血间充质干细胞磁探针标记和MR成像研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2005,39(1):101-106.
[39] Hauger O, Frost EE, van Heeswijk R,et al.MR evaluation of the glomerular homing of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of nephropathy.Radiology. 2006; 238(1):200-210.
[40] Gao F, Kar S, Zhang J,et al.MRI of intravenously injected bone marrow cells homing to the site of injured arteries.NMR Biomed. 2007;20(7):673-681. |
| [1] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [2] | Li Su-juan, Yuan Wen-chang, Mai Yun-pei, Hou Ning. Adenoviral vectors carrying Brahma-related gene 1 attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6021-6027. |
| [3] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [4] | Jing Cai-xia, Liu Chang-kui, Tan Xin-ying, Luo Jin-chao, Hu Min. Bone mesenchymal stem cells with allogeneic bone to repair canine mandibular defects: detection of osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2138-2143. |
| [5] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [6] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhang Ya-xiao, Zhang Bing, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Wang Ren-feng, Liu Jia-bao, Wu Lin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of emphysema: intravenous versus intratracheal approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2211-2215. |
| [7] | Liang Jian-ji, He Zhi-yong, Liu Kang, Li Xiao-ling, Cheng Wei-min, Yu Xin-ping, Chen Er-dong. Intraarticular injection of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for mild-to-moderate osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2216-2223. |
| [8] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [9] | Liang Liang, Xu Tao, Song Yang, Sheng Wei-bin. siRNA lentiviral vectors carrying telomerase reverse transcriptase gene hasten astrocytes apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1707-1711. |
| [10] | Han Xiang-zhen, He Hui-yu, Hu Yang, Ba Jiao-jiao, Wang Huan-huan, Mi Xue, Abulizi•Abudula. Recombinant lentiviral vector transfected sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic gene expression changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 821-828. |
| [11] | Huang Jian-feng, Huang Ji-feng, Zhang Wei-cai. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells induced by combination of two cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 829-834. |
| [12] | Zou Bin, Zong Shao-hui, Zeng Gao-feng, Fang Ye, Gao Tai-hang. Effects of alpha-zearalanol on the osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 835-840. |
| [13] | Yang Yi, Ding Wen-jing, Dong Wan-li. Autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 expression in neuron-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 841-846. |
| [14] | Su Xue-lian, Bao Guang-jie, Kang Hong, Liu Lin, Kong Nan-nan. Morphological changes of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into fibrochondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 860-865. |
| [15] | Nie De-zhi, Wan Ying, Ben Liang, Wang Ying-jun, Liu Xiang-zhu, Wang Li-hui, Li Chao, Zhang Shi-dong. Stem cell tumorigenicity in Balb/c nude mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 888-893. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||